As an authorized distributor, MD Scientific can offer Tosoh Bioscience’s comprehensive line of high and low pressure columns to meet your purification needs. Please contact us for advice on which column to choose.
For more details and price, please contact MD Scientific at info@md-scientific.dk or +45 7027 8565
TSKgel® HPLC Columns
Tosoh Bioscience offers a comprehensive line of high and low pressure columns to meet your purification needs. TSKgel columns stand out in all modes of liquid chromatography, from Ion Exchange to Hydrophobic Interaction, from Affinity to HILIC, from Ion Chromatography to Reversed Phase, from HPLC to FPLC, from Analytical to Prep.

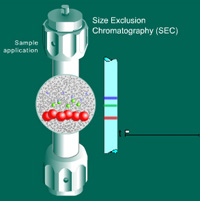
Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC)
separates molecules based on their size, or more precisely, their hydrodynamic volume. It is based on the discrimination of individual sample components by the pores of the packing material. Large sample molecules cannot or can only partially penetrate the pores and elute from the column first, whereas smaller molecules can access all or a larger number of pores and elute later. SEC is the only mode of chromatography that does not involve interaction with a stationary phase by means of adsorption or partitioning of the solutes.
The terms SEC, GFC (gel filtration chromatography) and GPC (gel permeation chromatography) all refer to the same chromatographic technique. In GFC an aqueous mobile phase is used, while an organic mobile phase is employed in GPC. The general term SEC covers both uses.
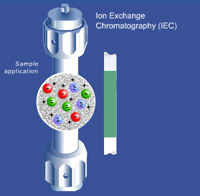
Ion Exchange Chromatography (IEC)
Separation in Ion Exchange chromatography (IEC or IEX) is based on reversible adsorption of charged solute molecules to immobilized functional groups of opposite charge. Biomolecules generally have charged groups on their surfaces, which change with the buffer pH. Elution can be accomplished by changing the ionic strength or the pH, of which changing the ionic strength by increasing the salt concentration is most common.
IEC is further subdivided into cation exchange and anion exchange chromatography. Anion and cation exchange phases are classified as strong or weak, depending on how much the ionization state of the functional groups vary with pH. A strong ion exchange phase has the same charge density on its surface over a broad pH range, whereas the charge density of a weak ion exchange phase changes with pH, affecting its selectivity, which differs at different pH values.
Hydrophobic Interaction Chromatography (HIC)
is based on non-polar interactions that are induced by high salt mobile phases. Stationary phases are similar to reversed phase chromatography (RPC) but the density of functional groups is lower. A weakly non-polar stationary phase is used with an aqueous mobile phase containing a high concentration of a chaotropic salt.
The technique is mainly applied to the separation of proteins, which are eluted by decreasing the salt concentration or by adding a low percentage of organic solvent. Although also based on hydrophobic interactions, selectivity in HIC separations is distinctly different from that in reversed phase chromatography. Despite the lower peak capacity in HIC compared to RPC, HIC has the advantage that the mobile phase conditions (primarily aqueous) do not usually disrupt higher-order protein structures.
Normal Phase and Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography (HILIC)
Normal phase and hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC) are primarily used to separate polar and hydrophilic compounds. In reversed phase mode very polar compounds are often not sufficiently retained in low percent organic, or even in 100% aqueous mobile phase. The order of elution in normal phase is opposite that found in reversed phase for the same mixture of compounds. Although non-polar organic mobile phases and a silica stationary phase were used traditionally in normal phase LC, today most separations are performed with aqueous-organic mobile phases and a more polar-bonded stationary phase. This mode of HPLC is now commonly referred to as HILIC, hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography.
By using an amide or amino bonded phase column, polar compounds can be retained by a normal phase or hydrophilic interaction chromatography retention mechanism. Typical mobile phases in HILIC are aqueous buffers with organic modifiers – primarily acetonitrile. In contrastto the retention behavior in reversed phase, in HILIC, solutes will be retained longer when increasing the percent acetonitrile.
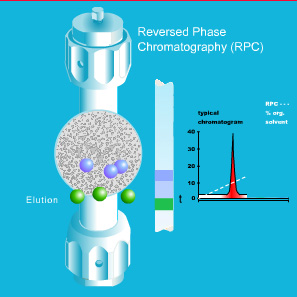
Reversed Phase Chromatography (RPC)
Starting in the mid 1970s Reversed Phase Liquid Chromatography (RPC) has become the standard technique to analyze small molecular weight compounds. More recently, RPC has become an accepted tool for the separation of peptides, proteins and other biopolymers in the pharmaceutical, chemical and biochemical industries.
RPC separates molecules based on nonpolar interactions and requires a nonpolar stationary phase and a polar mobile phase. Typically the mobile phase consists of a mixture of water (buffer) and acetonitrile, methanol, THF, or 2-propanol.
offers the greatest potential specificity and selectivity for the isolation or purification of biomolecules. Almost all biological molecules can be purified on the basis of a specific interaction between their chemical or biological structure and a suitable affinity ligand.
In AFC, the target molecule is specifically and reversibly adsorbed by a complementary ligand and immobilized on a matrix. Examples of a complementary ligand include an inhibitor, substrate analog or cofactor, or an antibody which specifically recognizes the target molecule. The selectivity is often based on spatial recognition, a ‘lock-and-key’ mechanism.
The adsorbed molecule is subsequently eluted either by competitive displacement or a conformation change through a shift in pH or ionic strength. Typical molecular pairs are antigens and antibodies, enzymes and coenzymes, and sugars with lectins. Purification of several thousand-fold may be obtained due to the high selectivity of the affinity interactions. Although affinity chromatography is not specific, in that no enzyme interacts with only one substrate, it is the most selective method for separating proteins.
FcR-IIIA Affinity
TSKgel FcR-IIIA-NPR is based on a recombinant Fc gamma IIIa receptor ligand immobilized on a non-porous polymer particle. It allows fast assessment of biologic activity of monoclonal antibodies.
Fc gamma IIIa receptor plays a key role in antibody-dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) which is a crucial mechanism of action of anti-tumor mAbs. The Fc-glycans of antibodies are known to play an important role in Fc-mediated effector functions. Hence, separation patterns of therapeutic antibodies on TSKgel FcR-IIIA-NPR can be correlated to Fc N-glycans and the ADCC activity of immunoglobulins. Early eluting peaks of TSKgel FcR-IIIA-NPR represent glycoforms with low ADCC activity while late eluting peaks represent glycoforms with high ADCC activity.
- Go to Tosoh Bioscience’s website for an overview of all columns.
- See catalogue of all types of HPLC columns Tosoh.
MD Scientific is authorised distributor in Denmark for Tosoh.
Showing 1–10 of 11 results